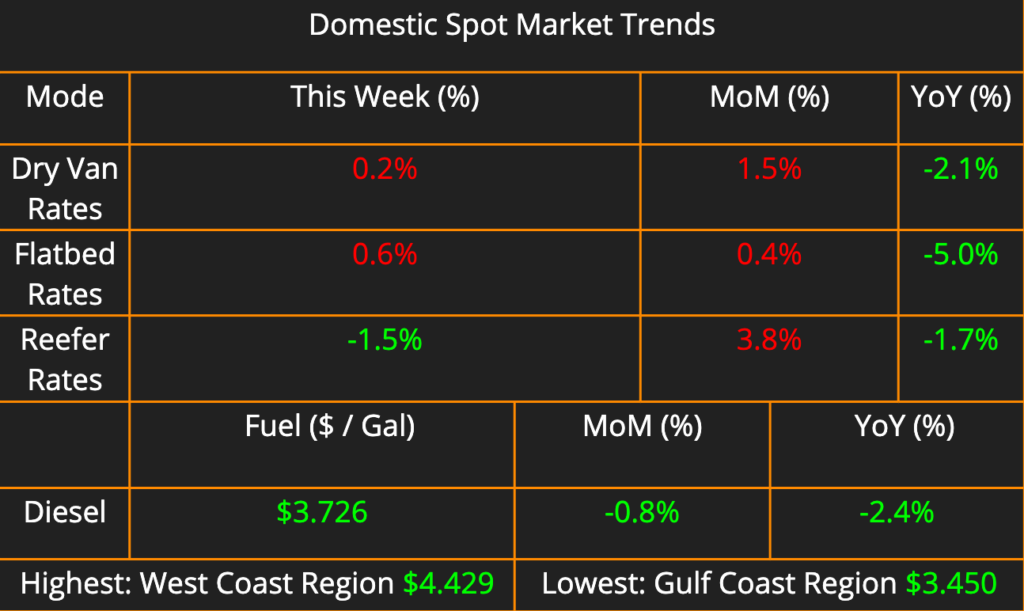
International shipping data is slightly delayed this month, look for updated port volume figures covering May’s activity in next week’s newsletter. Dry van and flatbed pricing saw a week of modest recovery with incremental rate hikes but remain down year-over-year (2.1% and 5.0%, respectively). Reefer rates, however, defied the trend, climbing nearly 4% month-over-month as the annual produce season strains capacity. Diesel prices continued their downward trajectory, falling another 0.8% this week compared to last.
This week’s transportation news navigates a complex landscape. U.S. Customs struggles to balance security with a surge in e-commerce imports, particularly from China, as relaxed duty-free thresholds raise concerns about unchecked goods. Meanwhile, the global ocean freight market braces for recent highs in June due to a confluence of factors – ongoing tensions, port congestion, and a pre-peak season rush. Finally, economic uncertainty fueled by war and inflation pushes cost savings back to the top of the agenda for procurement executives in 2024. While prioritizing efficiency, reports suggest a focus on long-term value creation alongside short-term cost-cutting measures.
De Minimis Threshold: Security Concerns Clash with Trade Facilitation
The surge in e-commerce imports, particularly from China, is posing a major challenge for U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). A key factor is the increased de minimis threshold, which raised the duty-free exemption for low-value shipments to $800 in 2016. This has fueled a dramatic rise in e-commerce imports, overwhelming CBP’s capacity to effectively screen them.
These concerns stem from the potential security risks associated with such a large volume of unchecked goods. Counterfeit products, fentanyl, and even goods made with forced labor are more easily entering the U.S. under the relaxed de minimis system. Furthermore, CBP has suspended several customs brokers for failing to properly classify and value goods or for late data filing, suggesting some may be exploiting loopholes in the system.
The sheer volume of e-commerce shipments has overwhelmed CBP, leading to delays and prompting them to crack down on non-compliant brokers. Adding to the complexity is the Entry Type 86 program, designed to expedite clearance for low-value shipments. However, the program has faced issues with inaccurate or incomplete data from filers, while brokers struggle to comply with stricter filing requirements.
This situation has also drawn the attention of lawmakers. Proposals are being considered to limit the de minimis benefit for Chinese imports or require more data for low-value shipments altogether. These proposals reflect concerns that China is exploiting the de minimis system to undercut U.S. businesses. However, increased scrutiny and potential changes to the system could raise costs for e-commerce businesses and consumers, particularly small businesses that operate on tight margins.
Finding a balance between security concerns and facilitating legitimate e-commerce is crucial. Potential solutions include improved data sharing between e-commerce platforms, sellers, and CBP. This could help identify suspicious shipments more effectively. Furthermore, developing risk profiles for e-sellers would allow CBP to focus enforcement efforts on those with a higher likelihood of non-compliance. Standardizing data requirements across different import types would also simplify compliance for brokers and sellers.
Ultimately, addressing the challenges of e-commerce imports requires a multi-faceted approach. Improved enforcement, data sharing, and clear regulations are all essential to ensure a balance between security, trade facilitation, and fair competition in the e-commerce landscape.
Ocean Freight Costs Poised to Exceed Red Sea Crisis Highs in June
The global ocean freight market is expected to undergo a significant cost increase in June, potentially exceeding the peak rates observed during the Red Sea crisis. This development is attributed to a confluence of factors creating a challenging environment for shippers.
- Persistent Red Sea Tensions: The ongoing conflict in the Red Sea continues to disrupt established trade routes, impacting global supply chains.
- Port Congestion Challenges: Ports worldwide are experiencing persistent congestion, leading to delays and bottlenecks in the movement of goods.
- Pre-Peak Season Rush: As the peak season for shipping approaches, shippers are accelerating cargo movement, further straining available capacity.
The anticipated cost increase will be most pronounced on major trade routes, particularly those connecting the Far East to the United States and Europe. Spot rates, which have surged for 10 consecutive weeks, according to ShippingWatch reporting, are projected to experience another significant rise. For instance, forecasts suggest a 57% increase in spot rates from the Far East to the US West Coast in June compared to May.
These developments are already impacting shippers. Even those with established long-term contracts are facing the possibility of “cargo rolling,” where shipping lines delay the movement of their cargo. Additionally, freight forwarders are encountering new surcharges and pressure to utilize more expensive expedited shipping options.
While there may be a possibility of slight improvement in the coming months, the near-term outlook for shippers remains challenging. The global ocean freight market is likely to experience a period of heightened costs and disruptions before a return to normalcy.
Procurement Chiefs Prioritize Cost Savings in Uncertain Economic Climate
A recent survey by The Hackett Group reveals a shift in priorities for procurement executives. According to their “CPO Agenda” report, cost savings have risen to the top of the list for 2024, a shift not seen since 2021. This renewed focus coincides with growing economic uncertainty, fueled by factors like the war in Ukraine and ongoing inflation.
The report underscores the proactive approach procurement teams are taking. Survey data indicates 75% of participants have developed plans to improve data and reporting – a key area for cost reduction. Hackett Group research further suggests a strong link between technology adoption and cost savings. Businesses deemed “technologically advanced” by the report enjoyed 96% higher savings compared to their less tech-savvy counterparts.
While cost reduction is the primary focus, the survey also highlights planned advancements in other areas. Over half of the participants indicated plans for improved strategic sourcing and supplier relationship management, suggesting a focus on long-term value creation alongside short-term cost savings.