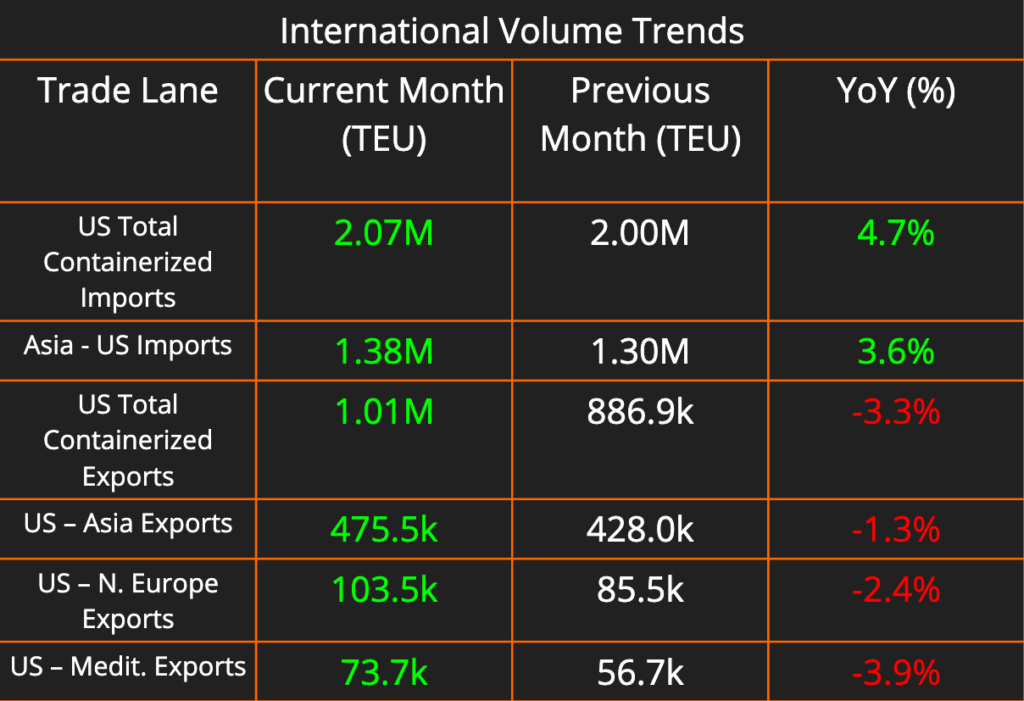
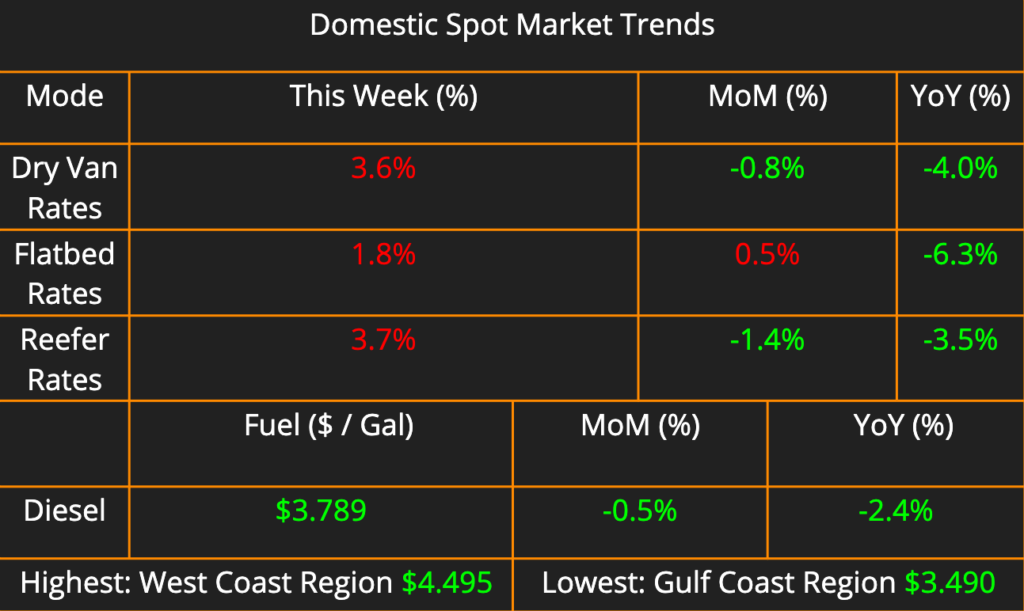
The shipping industry is experiencing a surge in activity, with import and export volumes climbing. Exports are showing particularly strong growth, up 14% month-over-month. Domestic pricing across all modes has risen steadily week-over-week, reflecting the tightening capacity observed in most markets over the past two weeks. Diesel prices, however, continue their decline, falling another 1.2% this week compared to last.
This week’s newsletter dives deep into two key issues impacting the transportation industry. First, we’ll explore the potential national consequences of California’s proposed ban on diesel locomotives. Then, we’ll shift gears and examine the upcoming contract negotiations between East Coast and Gulf Coast port unions, highlighting the potential impact on global supply chains.
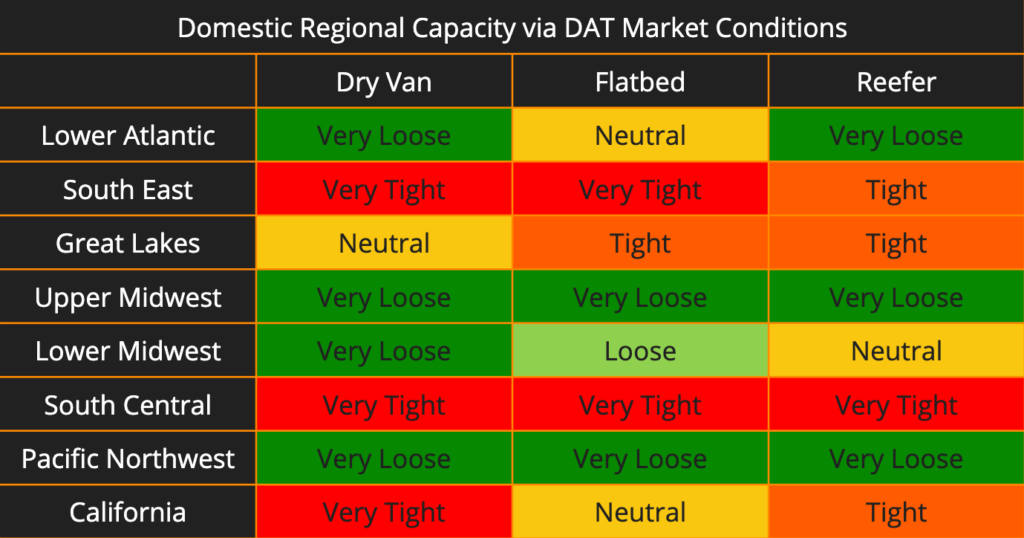
All regions have remained stable since our report last week, with limited changes. Flatbed capacity in the Lower Atlantic upgraded from Very Loose to Neutral. Reefer capacity in California downgraded from Very Tight to Tight. Overall, we are still seeing core produce regions tight in capacity and likely will continue to see tight capacity through the remainder of the summer.
California’s Diesel Locomotive Ban Faces National Backlash
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has proposed a regulation to phase out diesel locomotives in the state, but it’s facing strong opposition from businesses, government officials, and industry groups across the nation. They argue the “In-Use Locomotive Regulation” would disrupt the national supply chain, raise prices, and force businesses to close.
The regulation has several key components. It mandates stricter idling times, requires the retirement of older locomotives within six years, and establishes a system where operators contribute to a “spending account” based on their emissions. Critics argue that these requirements are unrealistic and financially burdensome.
Hundreds of comments submitted to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) highlight concerns about the regulation’s impact. Businesses and elected officials from nearly every state are urging the EPA to reject CARB’s request for approval. They point out that locomotives are often used across state lines, and a California-specific regulation would disrupt the entire national rail network. Additionally, the high cost of compliance could force smaller railroad companies out of business, further hindering the supply chain.
Opponents also argue that the technology required by the regulation isn’t yet commercially viable, and there’s not enough manufacturing capacity to meet the proposed deadlines. Furthermore, the regulation doesn’t consider the long lifespan of locomotives, which are typically multi-million dollar assets used for decades.
With widespread opposition and concerns about practicality, the EPA faces a difficult decision when considering whether to approve CARB’s regulation. The potential environmental benefits of cleaner locomotives will need to be weighed against the potential economic disruption and strain on the national supply chain.
Port Talks Poised to Set the Stage for Global Supply Chains
The ocean container shipping industry has witnessed sudden and dramatic increases in shipping rates, prompting speculation and analysis across the supply chain landscape. Several factors contribute to this surge, and one significant element is the imbalance between container demand and vessel capacity, exacerbated by the global economic rebound post-pandemic. These shortages can partly be attributed to the flight of demand from West Coast ports last summer during the West Coast longshoreman union talks, when shippers feared disruptions potentially caused by negotiation tactics.
In recent weeks, negotiations between East Coast and Gulf Coast port unions and the United States Maritime Alliance (USMX) have taken center stage in the realm of international shipping. Negotiations are currently underway, with a deadline of September 30th, 2024 looming for a new contract to be agreed upon. Both sides have expressed confidence in reaching a deal, but the stakes are high, as any disruptions could further strain already stressed supply chains. At the heart of the discussions are crucial issues such as wages, benefits, and the integration of automation within port operations. For companies deeply entrenched in international commerce, the outcome of these negotiations holds substantial importance. Disruptions to port activities could result in delays in receiving essential raw materials and fulfilling customer orders, impacting supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The negotiations come at a time when global supply chains are already grappling with significant challenges, including the aforementioned port congestion and container shortages. As such, the potential outcome of these talks has heightened concerns among stakeholders across industries, particularly due to the wariness following the West Coast talks last year. A shift in labor agreements or port productivity could reshape the landscape of international trade, influencing shipping schedules, costs, and overall supply chain resilience. Overall, both parties express confidence in reaching a favorable agreement, highlighting the importance of maintaining stability and building greater automation and efficiency in port operations.